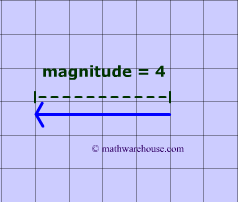
A Vector is something that has two and only two defining characteristics.
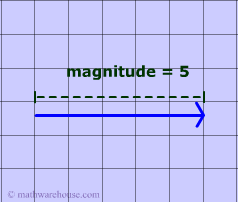
Magnitude is "how large' something is . In the diagrams 1 and 2, you can see vectors that have magnitudes of 4 and of 5.

The meaning of direction is pretty self explanatory. The vector must start somewhere and move in a path towards a different place. In diagrams 3 and 4 , the green dashed line represents the direction of the vector.
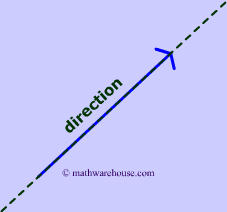
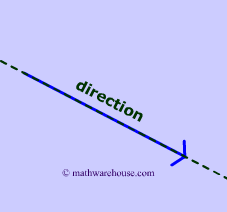
Answer: --> not have a direction. All that we know from the speed is the magnitude of the movement. This is not a vector. Remember a vector needs 2 and only 2 things (magnitude and direction) --> direction - west. Now, we have a vector. In physics, it's called a velocity (speed and direction). For our purposes, we now have a vector. -->
| Examples of Vectors | Non Examples |
|---|---|
| 4 units long at 30 $$^$$ | 4 unit |
| 44 miles per hour east (velocity) | speed of 44 mph (speed) |
Describe using compass directions (North, South, East, West) the direction of the vector pictured below.